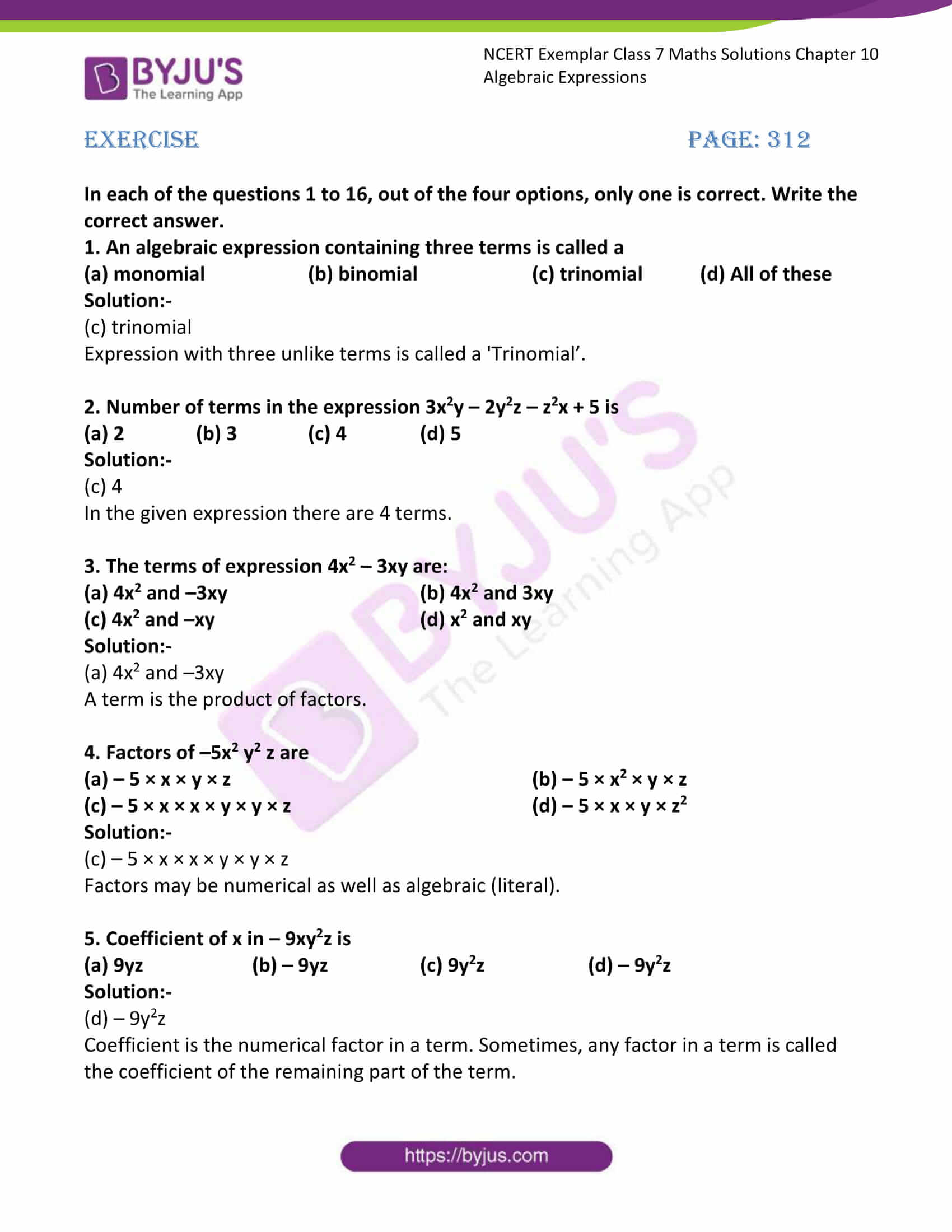
Factorise how to factorise 2 (xyab)x^2y^2a^2b^2 2x (ab)3y (5a5b)4z (2b2a) Solve x^33x^23x1 divided by x1 Factorize by grouping method 16 (ab)4a4b factorise2 (2x5y) (3x4y)6 (2x5y) (xy) Rich Text Editor, question_dataSep 16, 08 · Favorite Answer ok, this is a experience type question, you won't actually factories it factors of the first one is really easy it has to contain factors of 27 which is only obtainable by 3 x 3 x 3 so ( x3) to start with then since you have a 2 in the DT X^3 one of the box is (2x3)X2 y2 = 1 xy Use Equation 2 to substitute into the equation for y '' , getting , and the second derivative as a function of x and y is Click HERE to return to the list of problems SOLUTION 14 Begin with x2/3 y2/3 = 8 Differentiate both sides of the equation, getting D ( x2/3 y2/3
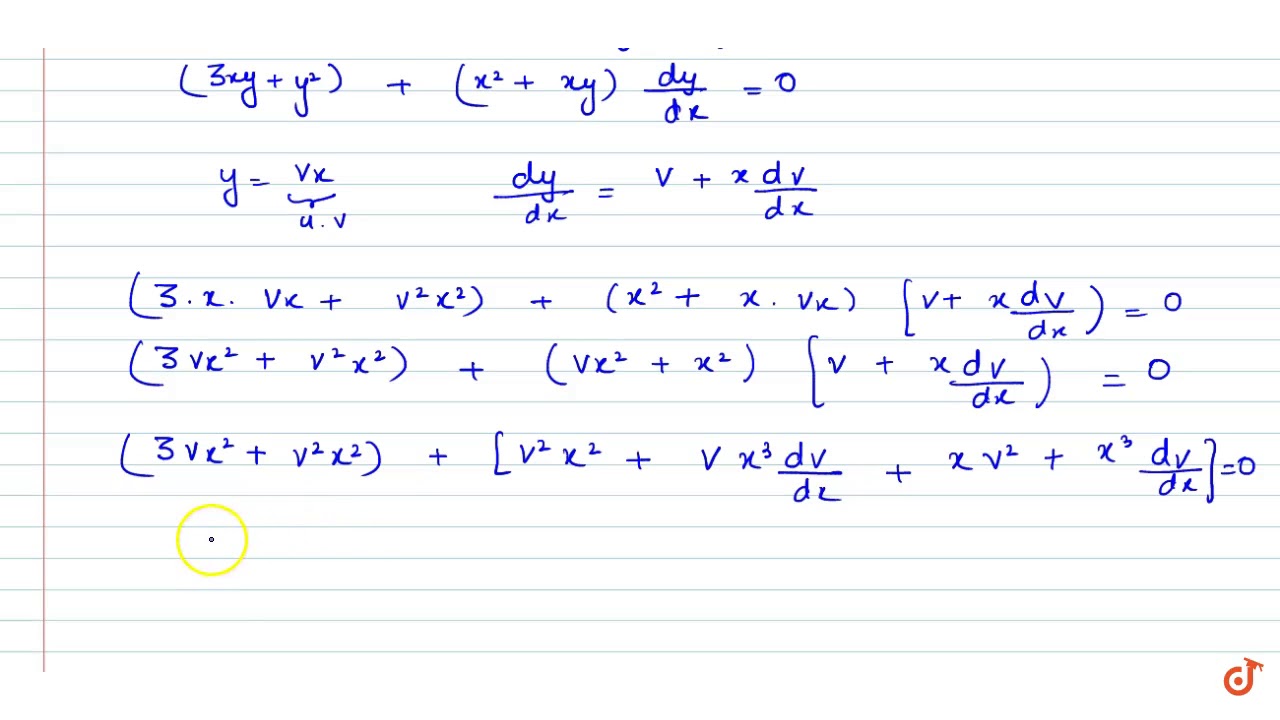
3x Y Y 2 Dx X 2 X Y Dy 0 Youtube
Factorise 3(x+y)^2-5(x+y)+2
Factorise 3(x+y)^2-5(x+y)+2-Factor $$3 x(2 a5 b)2 y(2 a5 b)$$ We notice that a common factor of each term is $2 a5 b$ When we factor out the $2 a5 b$ from the first term, there is a $3 x$ left When we factor out the $2 a5 b$ from the second term, there is a $2 y$ left Our final factored form is $(2 a5 b)(3 x2 ySolution for y=3 (x5) (x2) equation Simplifying y = 3 (x 5) (x 2) Reorder the terms y = 3 (5 x) (x 2) Reorder the terms y = 3 (5 x) (2 x) Multiply (5 x) * (2 x) y = 3 (5 (2 x) x (2 x)) y = 3 ( (2 * 5 x * 5) x (2 x)) y = 3 ( (10 5x) x (2 x)) y = 3 (10 5x (2 * x x * x)) y = 3 (10 5x (2x x 2 )) Combine like terms 5x 2x = 3x y = 3 (10 3x x 2 ) y = (10 * 3 3x * 3 x 2 * 3) y = (30 9x 3x 2 ) Solving y



Solve X Y 14 X Y 2
Get FREE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 25 We have created Step by Step solutions for Class 9 maths to help you to revise the complete Syllabus and Score More marks Factorise 27x 3 y 3 z 3 – 9xyz Solution 27x 3 y 3 z 39xyz = (3x) 3 y 3 z 33(3x)(yFactorization of x 3 y 3 It can be seen in most book that x 3 y 3 can be factorized by dividing the expression by (x y) After division we get a quotient of (x 2 xy y 2) with no remainder Therefore However, this method involves knowing the factor (x y) beforehand (and the understanding of Factor Theorem)Jul 31, 13 · Factorise 2x^2 5x 3 Determine if its a growth or decayThen find the percent increase of decrease 1y=16(25)^x 2y=08(128)^x 3y=17(1/5)^x''
This problem has been solved!Nov 29, 15 · (x^3y^3)=(xy)(x^2xyy^2) This is a sum of cubes This is a semiimportant identity to know (x^3y^3)=(xy)(x^2xyy^2) Although it doesn't apply directly to this question, it's also important to know that (x^3y^3)=(xy)(x^2xyy^2) This gives us the rule (x^3y^3)=(xy)(x^2∓xyy^2)Dear friend x³5x²x5 => x³x5x²5 => x(x²1)5(x²1) => (x5) (x²1) I hope it's help you please mark me as brainlist Bolna
Express the middle term and the constant in terms of these numbers mathx^2 2\sqrt {5}x 3 = /math Continue Reading You do it the usual way The coefficient of the middle term is negative, but the constant term is positive Hence, you must look for two numbers whose sum is math2\sqrt {5} /math and product is math3 /mathFactorcalculator factor 3x^{2}5x2 en Related Symbolab blog posts Middle School Math Solutions – Equation Calculator Welcome to our new "Getting Started" math solutions series Over the next few weeks, we'll be showing how SymbolabFactor completely 3 x^{2}5 x y^{2}2 y^{4} Join our Discord to get your questions answered by experts, meet other students and be entered to win a PS5!



Factorise X 3 3x 2 9x 5



Fiches D Exercices Developpement Et Factorisation
Factorize 6x^2 5x6 The quotient obtained on dividing x square 4 by x 2 is Factorise 6x25x6 using factor theorem factorise x square 1/x square 6 factorise 2xsqure7x3 what do you meant by zeros of polynomial 25xsq35x12Solution Steps x ^ { 3 } 2 x ^ { 2 } y x y ^ { 2 } x 3 − 2 x 2 y x y 2 Factor out x Factor out x x\left (x^ {2}2xyy^ {2}\right) x ( x 2 − 2 x y y 2) Consider x^ {2}2xyy^ {2} Use the perfect square formula, a^ {2}2abb^ {2}=\left (ab\right)^ {2}, where a=x and b=yThe two terms, 2(x – y) and –b(x – y), do indeed have a common factor;



10 Without Actually Calculating The Cubes Find The Value Of 48 3 30 3 18 3 N11 The Volume Of



Example 14 Divide 24 X 2yz Xy 2z Xyz 2 By 8xyz Using Both
I wanted to post the factorisation of x^2 y^2 as a hint, because once that is factored, the rest is trivial Or so I thought Hint 2 There is another x y in the expression $\endgroup$ – gnasher729 Sep 7 '16 at 1518Namely, the parenthetical factor x – y This binomial may be different from what I'm used to seeing referred to as being a "factor", but the factorization process works just the same for this expression as it did for every other expression beforeFactorise the following expressions 3 x 2 − 5 x y − 1 2 y 2 Medium Answer 3 x 2 − 5 x y − 1 2 y 2 = 3 x 2



Developper Et Factoriser Une Equation Superprof
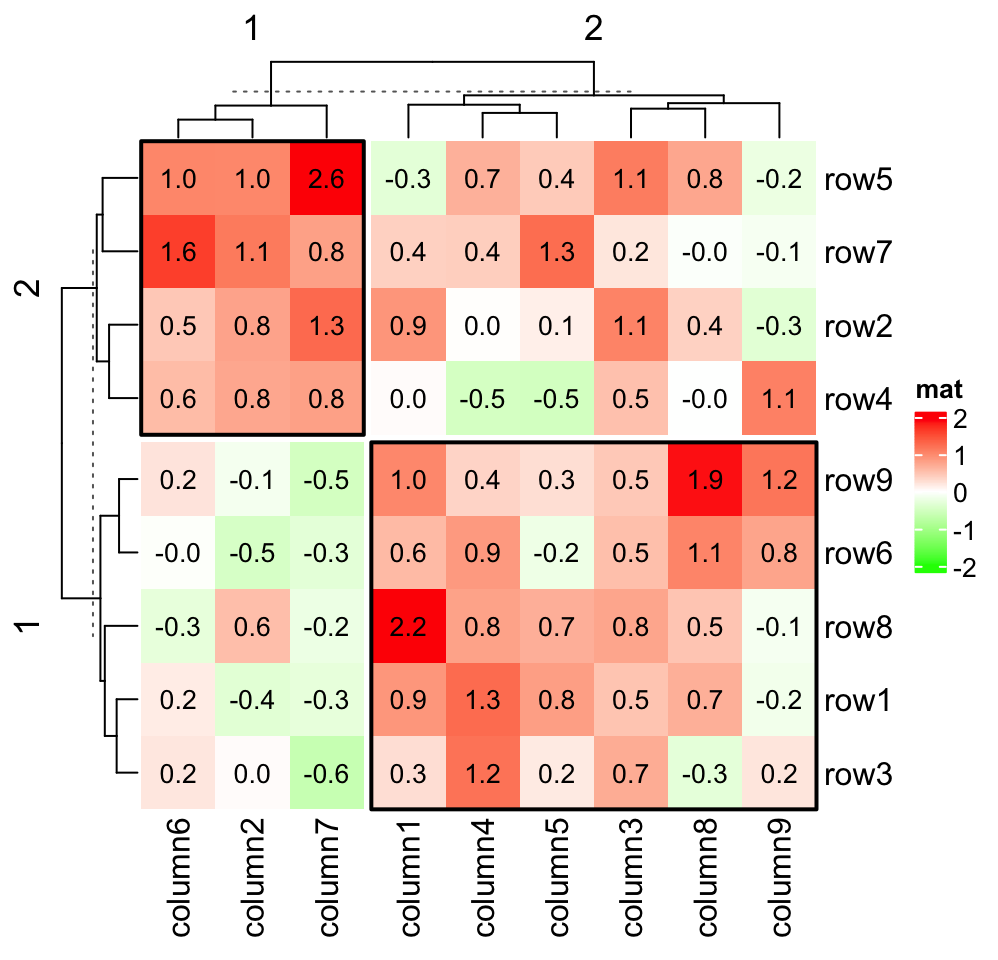


Chapter 2 A Single Heatmap Complexheatmap Complete Reference
Factorise the given question 1 3x2y^2 5x2y2 Dear student Question is wrong Please check and repost this You can qlso attach an image I will be hapFeb 21, 17 · Explanation The standard form of the quadratic function is y = ax2 bx c To factorise the function • consider the factors of the product ac which sum to give b for 2x2 5x − 3 a = 2,b = 5 and c = − 3 ⇒ ac = 2 × − 3 = − 6 the required factors of 6 are 6 and − 1Question 17 Consider the following formula y=3(x5)(x2) Which of the following formulas is equivalent to this one?



Ex 14 3 4 Ii Divide As Directed 26xy X 5 Y 4 13x Y 4



Factorize 5 3x Y 2 6 3x Y 8 Brainly In
Equation at the end of step 2 (((3•(x 2))xy)(2•(y 2))) (((5•(x 2))5xy)(2•5y 2)) ————————————————————————•———————————————————————— ((x 3)(y 3)) (15x 2 10xy) Step 3 Equation at the end of step 3For factoring x3 −6x2 3x10, we should know atleast one zero of this polynomial Once we know it, we can divide the polynomial by the factor to find the quotient and factor the quotient further to find other zeroes so, (x−2) is a factor So, the zeroes of polynomial x= −1,2In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind For example, 3 × 5 is a factorization of the integer 15, and (x – 2) (x 2) is a factorization of the polynomial x2 – 4



Factorize 4 X Y 2 12 X Y X Y 9 X Y



Developper Reduire Et Factoriser En Mathematiques
Question_answer Answers (2) edit Answer person Kishore Kumar Consider, 3 (x y) 2 – 5 (x y) 2 = 3 (x y) 2 – 3 (x y) – 2 (x y) 2 = 3 (x y) (x y) – 1 – 2 (x y) – 1 = (x y) – 1 3 (x y) – 2 = x y – 1 3x 3y – 2View virtualassignment2 (3)docx from TDV 101 at Wilson High School Name London Coker_ Block _ Factoring 1 5 b2 13 b6 2 9 x 2−26 x−3 3 15 〖−2 x−x 〗2 4 x 6−〖 3 x 〗3 y−〖10Telangana SCERT Class 9 Math Chapter 2 Polynomials and Factorisation Exercise 25 Math Problems and Solution Here in this Post Telanagana SCERT Class 9 Math Solution Chapter 2 Polynomials and Factorisation Exercise 25



Root Thistpainter Class Reference
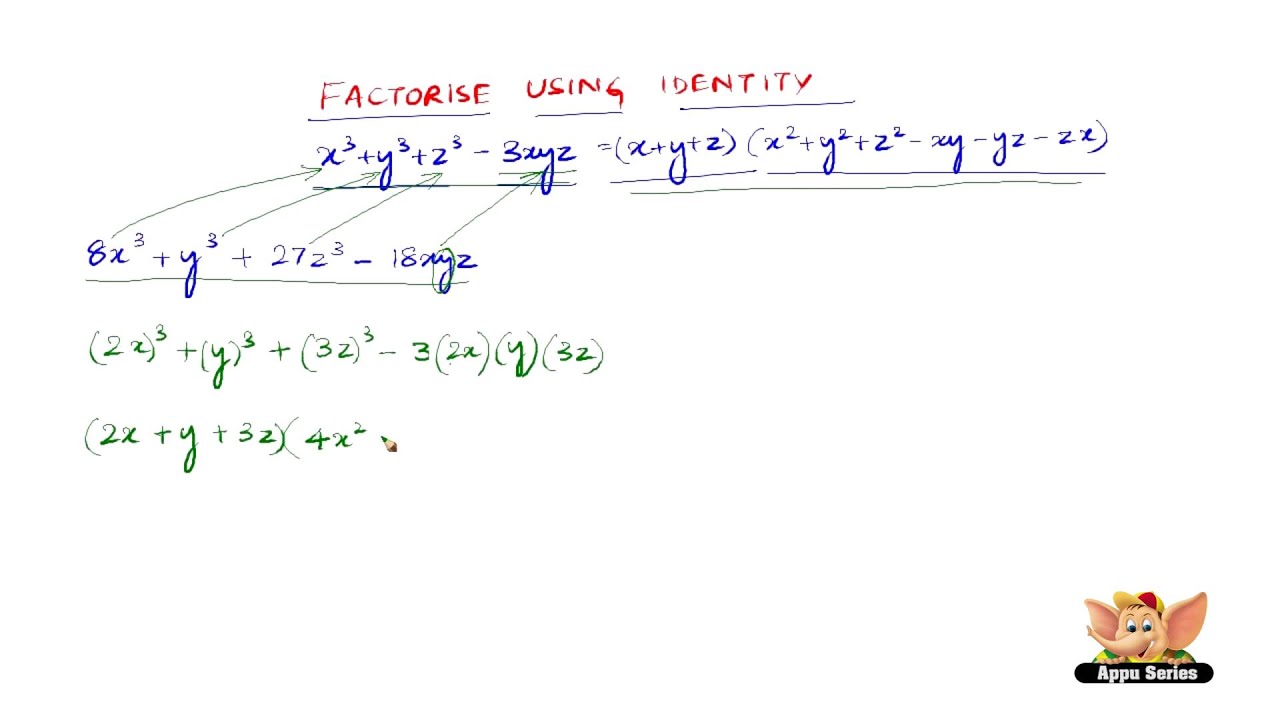


How To Factorise Using The Identity X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube
Jan 27, · Free Online Scientific Notation Calculator Solve advanced problems in Physics, Mathematics and Engineering Math Expression Renderer, Plots, Unit Converter, Equation Solver, Complex Numbers, Calculation HistoryDec 08, 16 · Transcript Example 14 Factorize y2 – 5y 6 by using the Factor Theorem Step 1 We check if y2 is multiplied by 1 y2 – 5y 6 Step 2 Writing y2 – 5y 6= (y – a) (y – b) So, ab = Constant term = 6 We find factors of 6 6 = 6 × 1 6 = 3 × 2 So, factors of 6 are 1, 2 and 3Factorise 2√3x2 X 5√3 CISCE ICSE Class 9 Question Papers 10 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 4 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos & Videos & Videos 246 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads Factorise 2√3x2 X 5√3 Mathematics Sum



What Should Be Taken Away From 3 X Square Minus 4 Y Square 5 X Y To Get Minus X Square Minus Y Brainly In



Example 14 Divide 24 X 2yz Xy 2z Xyz 2 By 8xyz Using Both
Consider x^ {2}y^ {2}xy22xy as a polynomial over variable x Find one factor of the form x^ {k}m, where x^ {k} divides the monomial with the highest power x^ {2} and m divides the constant factor y^ {2}y2 One such factor is xy1 Factor the polynomial by dividing it by this factorMay 29, 18 · Ex 25, 5 Factorise 4x2 9y2 16z2 12xy – 24yz – 16xz 4x2 9y2 16z2 12xy – 24yz – 16xz = 22 x2 32 y2 42 z2 12xy – 24yz – 16xz = (2x)2A Factorise 125(x y)3 (5y 3z)3 (3z 5x)3 B Factorise 3(x y)2 5(x 2y) 2 Maths Polynomials



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 7 Factorization Download Free Pdf



Identify The Terms And Their Factors In The Following Expressions
Get the answer to Factor 2x^25x3 with the Cymath math problem solver a free math equation solver and math solving app for calculus and algebraFree equations calculator solve linear, quadratic, polynomial, radical, exponential and logarithmic equations with all the steps Type in any equation to get the solution, steps and graphHow to factor expressions If you are factoring a quadratic like x^25x4 you want to find two numbers that Add up to 5 Multiply together to get 4 Since 1 and 4 add up to 5 and multiply together to get 4, we can factor it like (x1) (x4)



3 Ways To Factor Algebraic Equations Wikihow



Simplify 2 X2 2xy 5 Xy Y2 Brainly In
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Factorise x^35x^2x5 Sanskarkumar Sanskarkumar Math Secondary School Factorise x^35x^2x5 2 See answers Brainly User Brainly User Hay!!This preview shows page 36 38 out of 59 pages Find and classify the critical points of the function f (x, y) = 2 x 3 x (4 y 3 9 y 2 6 y) Solution ∂f ∂x = (4 y 3 9 y 2 6 y) 6 x 2 ∂f ∂y = (12 y 2 18 y 6) x = 6(2 y 1)(y 1) x = 0 when y = − 1 or y = − 1 / 2 or x = 0 At y = − 1, ∂f ∂x = (− 4 9 − 6) 6 x 2 = 0 = ⇒ x 2 = 1 / 6 or x = ± 1 / √ 6Factor x^3y^3 x3 − y3 x 3 y 3 Since both terms are perfect cubes, factor using the difference of cubes formula, a3 −b3 = (a−b)(a2 abb2) a 3 b 3 = ( a b) ( a 2 a b b 2) where a = x a = x and b = y b = y



Answers
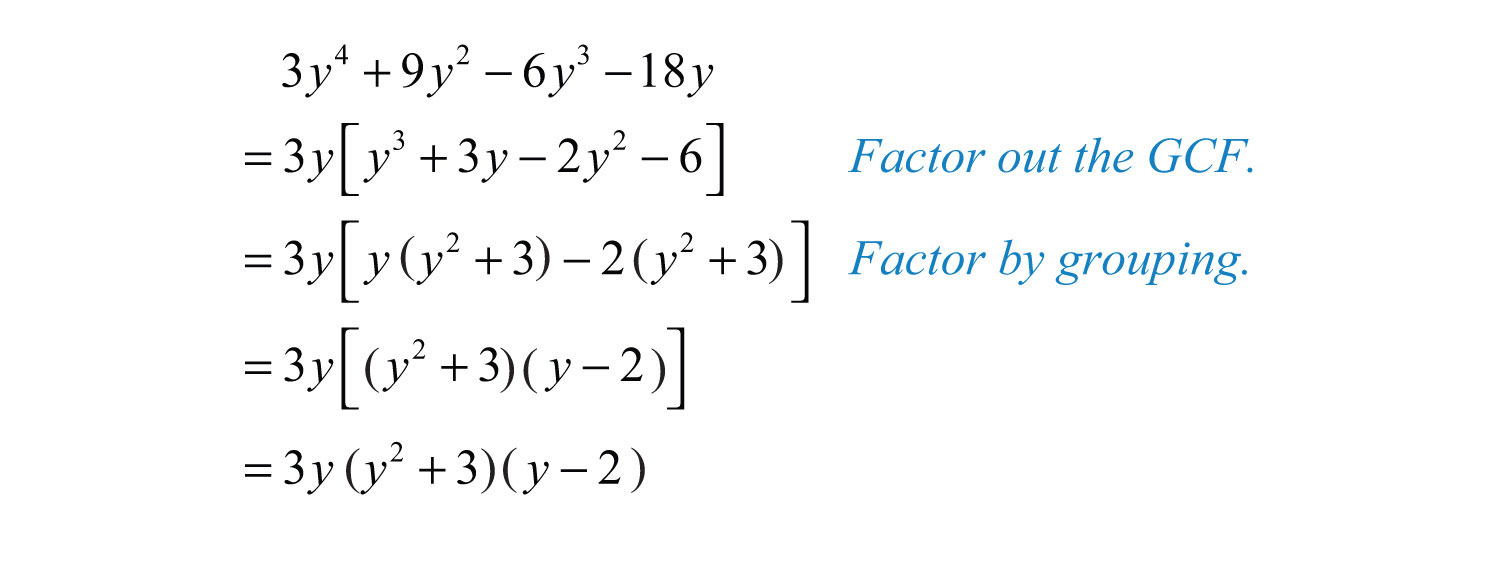


Factoring By Grouping Algebra Socratic
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music61 Adding fractions which have a common denominator Combine the numerators together, put the sum or difference over the common denominator then reduce to lowest terms if possible 3x2 5xy 3x2 5xy ————————— = ————————— 2 2Jun 18, 10 · An easy way to factor is to multiply the outside coefficients and alter the quadratic to x^2 5x 6 Now find two factors of 6 that add up to 5 (the middle coefficient) You then get (6) (1) The quadratic expression becomes 3x^2 6x 1x 2
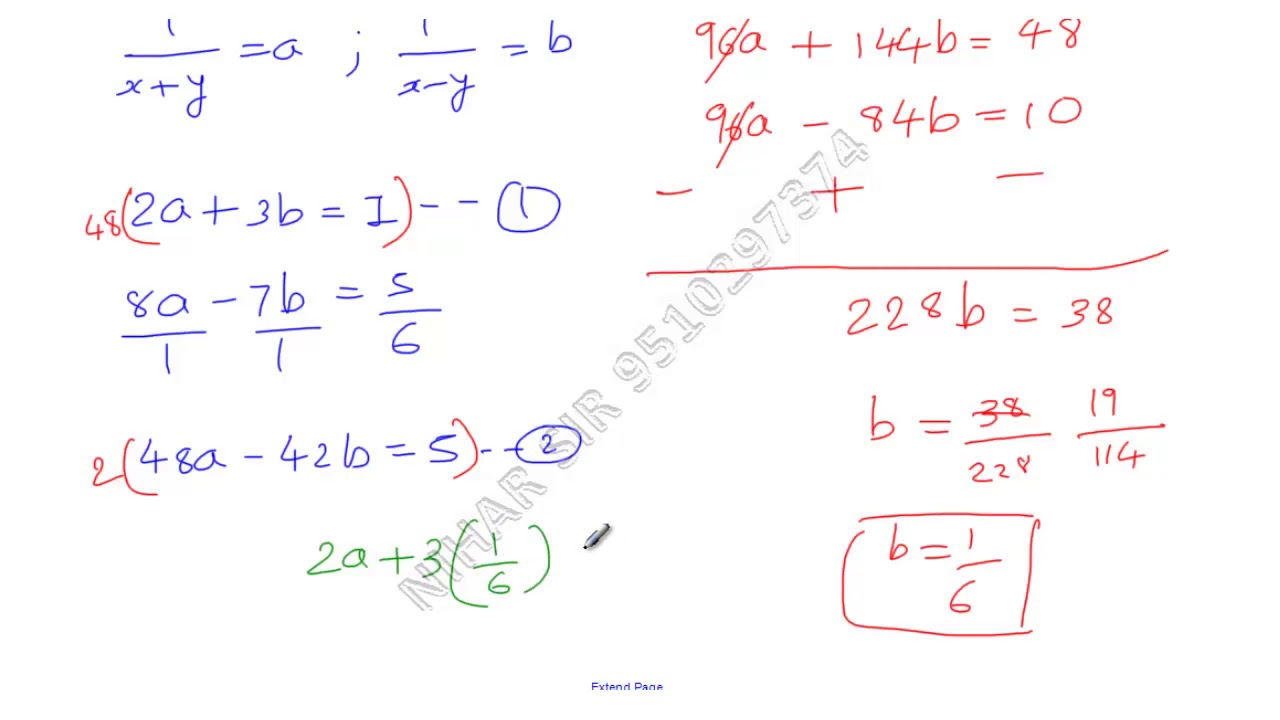


2 X Y 3 X Y 1 8 X Y 7 X Y 5 6 Solve X And Y Youtube



Factorise I A 2 A B 3 A 3 B Ii X 2 Y X Y 2 5 X 5 Y Iii A 2 A B 1 B B 3 Fiv X Y 2 X 1 Y 1
Algebra Factor x^2y^2 x2 − y2 x 2 y 2 Since both terms are perfect squares, factor using the difference of squares formula, a2 −b2 = (ab)(a−b) a 2 b 2 = ( a b) ( a b) where a = x a = x and b = y b = yAlgebra Calculator is a calculator that gives stepbystep help on algebra problems See More Examples » x3=5 1/3 1/4 y=x^21 Disclaimer This calculator is not perfect Please use at your own risk, and please alert us if something isn't working Thank youFactorise X^2 1/X^2 3 CISCE ICSE Class 9 Question Papers 10 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 5 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos & Videos & Videos 241 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads Factorise X^2 1/X^2 3 Mathematics Sum



Ex 2 5 8 Factorise I 8a3 12a2b 6ab2 Class 9



Factoring Using The Perfect Square Pattern Video Khan Academy
A(3a2) Now replace a by (xy) and expression becomes (xy)(3(xy)2) = (xy)(3x3y2) If you recognize that (xy) is a factor throughout you can immediately pull it out (xy) and then divide the expression by the factor and put the result in brackets following (xy) getting (xy)(3(xy)2) = (xy)(3x3y2)3 Consider the differential equation (x^2 y^2 − 5) dx = (y xy) dy (a) Verify that the DE is not exact (b) Solve the DE by finding an appropriate integrating factorA y=3x29x30 B y=x23x10 C y=3x23x10 D y=3x23x30 I would like you to show me the steps to solving this problem



Identify The Like Terms In Each Of The Following Algebraic Expre



Pdf Print Complete Mathematics For Cambridge Igcse Fifth Edition Extended Cambridge Igcse Mathematics Igcse Maths



Factorise 3 X Y 2 5 X Y 2 Brainly In



Factorise 3 X Y 2 5 X Y 2 Brainly In



Factorise X Y 2 7 X 2 Y 2 12 X Y 2 Youtube
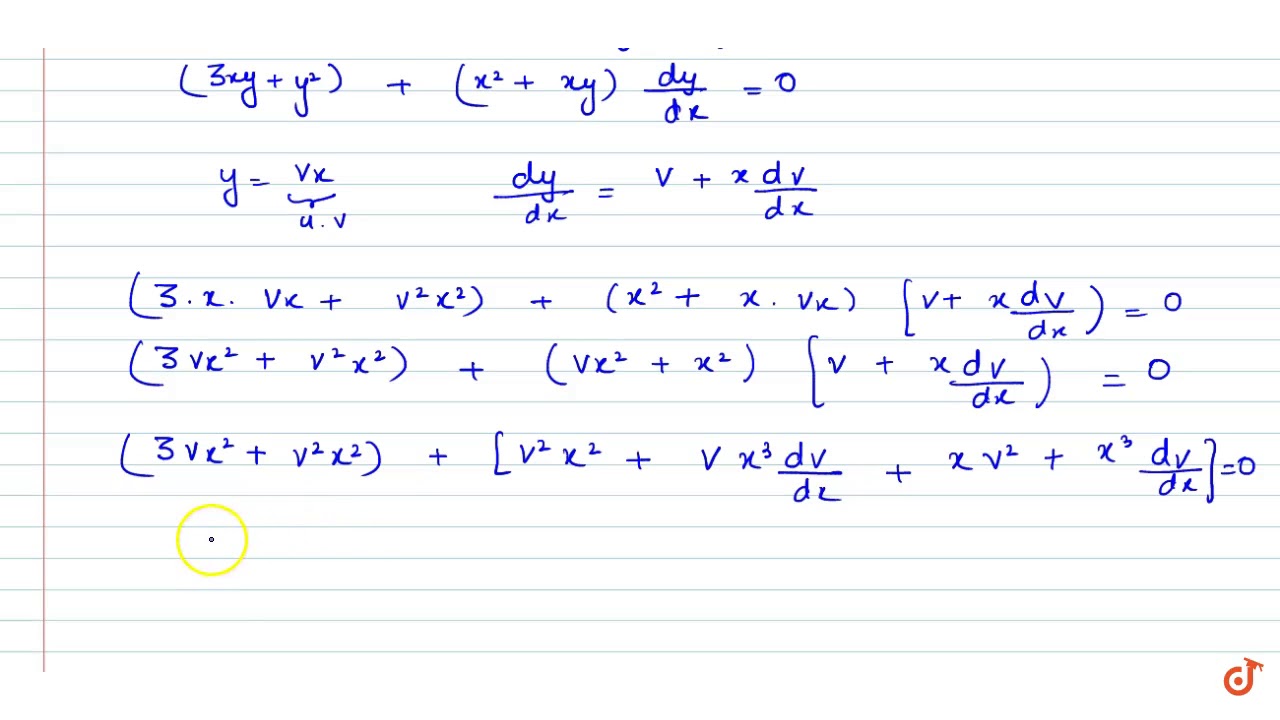


3x Y Y 2 Dx X 2 X Y Dy 0 Youtube



Ex 2 5 9 Verify I X3 Y3 X Y X2 Xy Y2 Ex 2 5
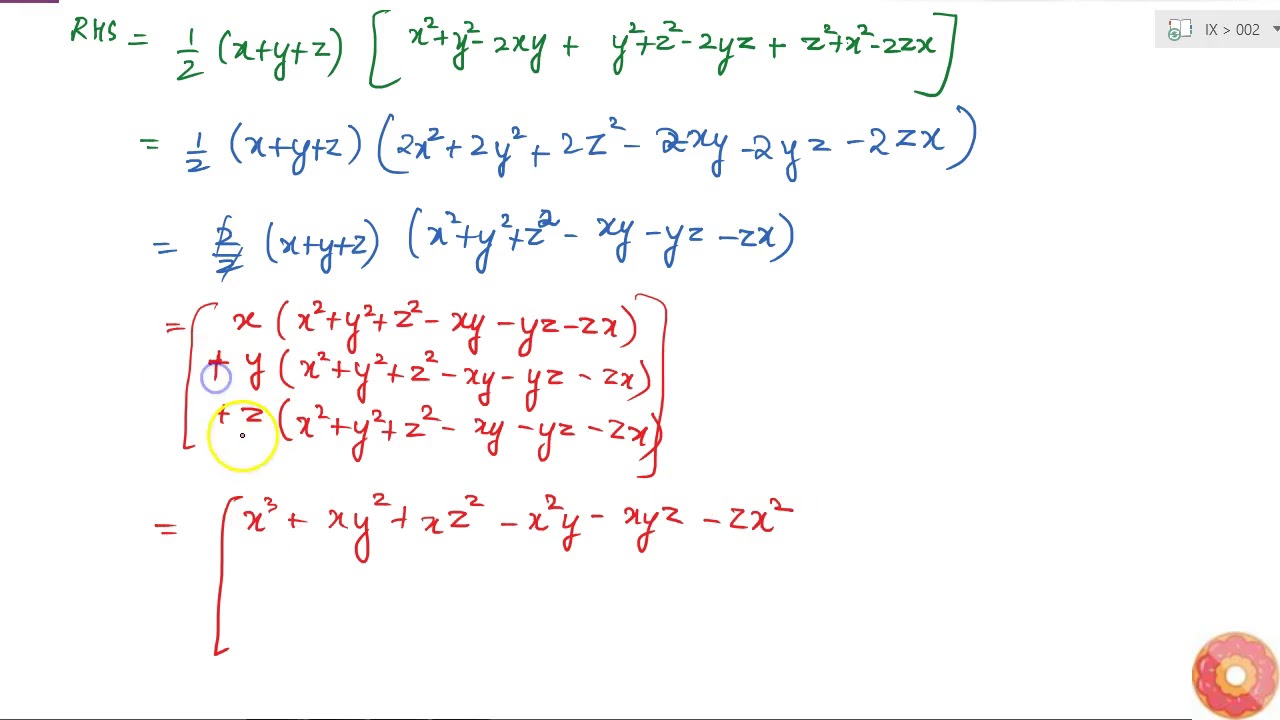


Verify That X 3 Y 3 Z 3 3x Y Z 1 2 X Y Z X Y 2 Y Z 2 Z X 2 Youtube



Factorise The Following Expressions Begin Array Ll Text I 5 X 2 25 X Y Text Ii 9 A 2 6 A X Text Ii 36 A 2 B 60 A 2 B C



Factorise 50 X Y 18 X Y Brainly In



If X 2 Y 2 49 And X Y 3 Then Find The Value Of X 3 Y 3



Solve X Y 14 X Y 2



Find The Answers To X Y Bracket X Minus Y Bracket Close 3 X Square Bracket Why Minus Y Square Brainly In



Factoring Two Variable Quadratics Rearranging Video Khan Academy



Ex 14 2 3 Iii Factorise 2x 3 2xy 2 2xz 2 Ex 14 2



Simplifying Radical Expressions



10 X Y 2 X Y 4 15 X Y 5 X Y 2 Solve The Simultaneous Equation Brainly In



Ex 14 1 2 Vi Factorise 5 X 2 Y 15 Xy 2 Chapter 14 Class 8



Factoring Using The Difference Of Squares Pattern Video Khan Academy



Ex 14 2 3 Iii Factorise 2x 3 2xy 2 2xz 2 Ex 14 2
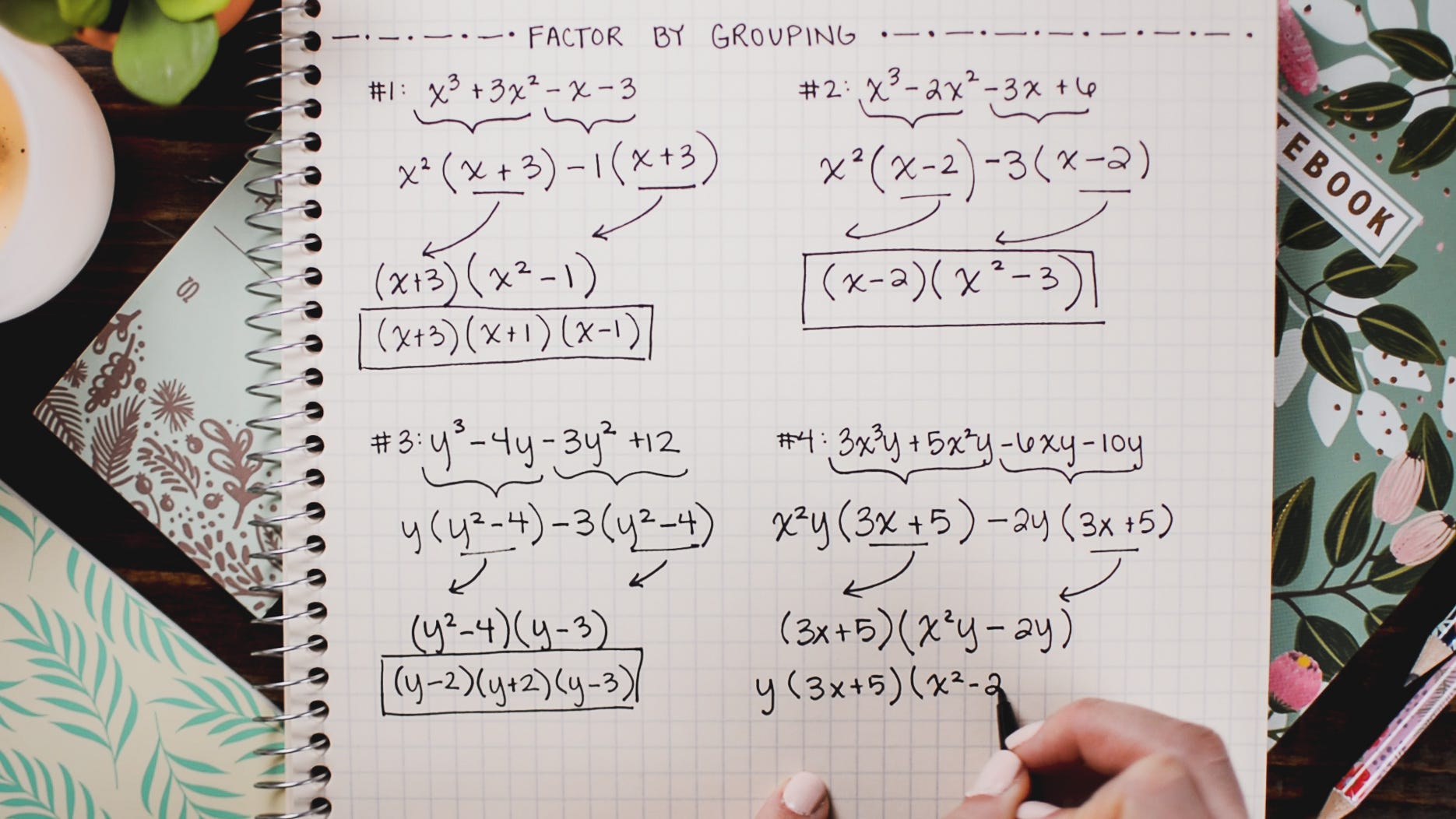


Starter Guide To Factoring Quadratics Polynomials By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium



Factorise 8x 3 27 Y 3 36 X 2y 54



The Factors Of X 3 X 2y X Y 2 Y 3 Are A X Y X 2 X Y Y 2 B X Y X 2 X Y Y 2 C Youtube



Expand Using Identities 3x 5y 2



Factorisation By Grouping The Terms X 2 3x 2 5 X 2 3x Y X 2 3



Find The Greatest Common Factor Gcf Hcf Of The Following Polyn



Factorize Each Of The Following Algebraic Expressions 5 X 2
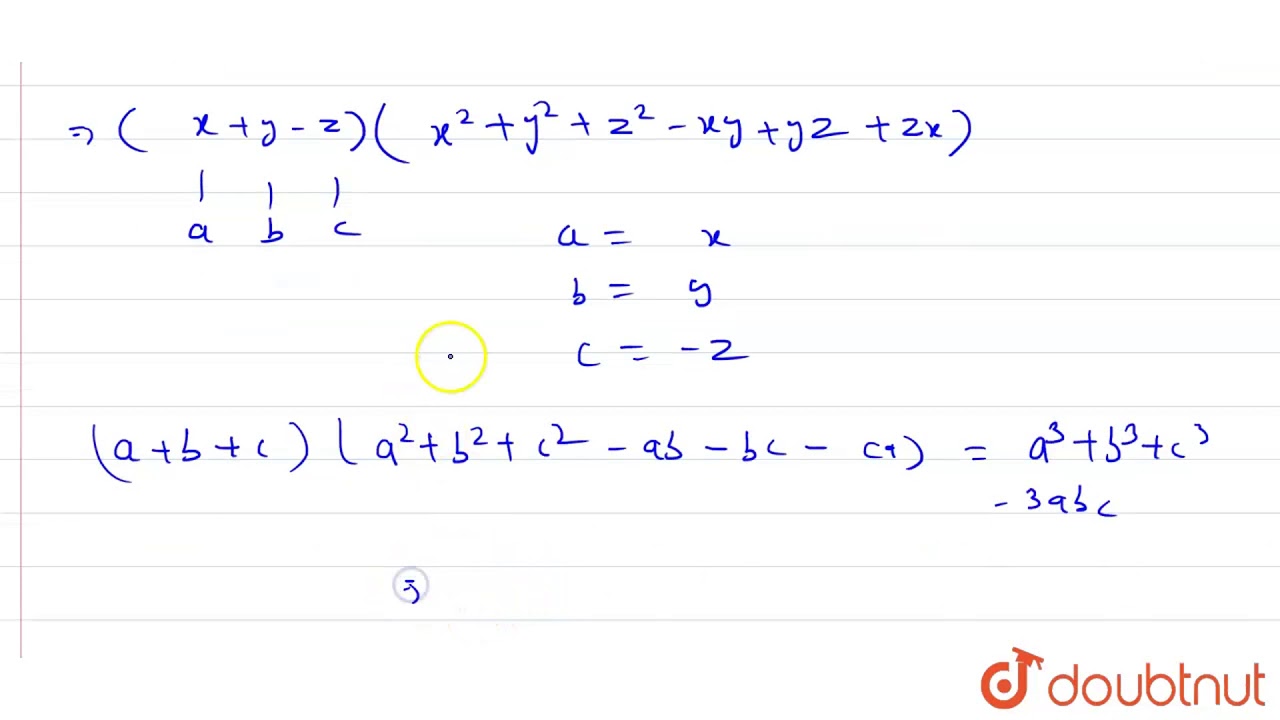


Find The Product X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube



Verify That X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz 1 2 X Y Z X Y 2 Y Z 2 Z X 2 Ieep2 Polynomial Mathematics Of Computing Learn All Concepts Of Polynomials Class 9 With Videos Diana Images



Preview Cambridge International As And A Level Pure Mathematics 1 Coursebook By Cambridge University Press Education Issuu
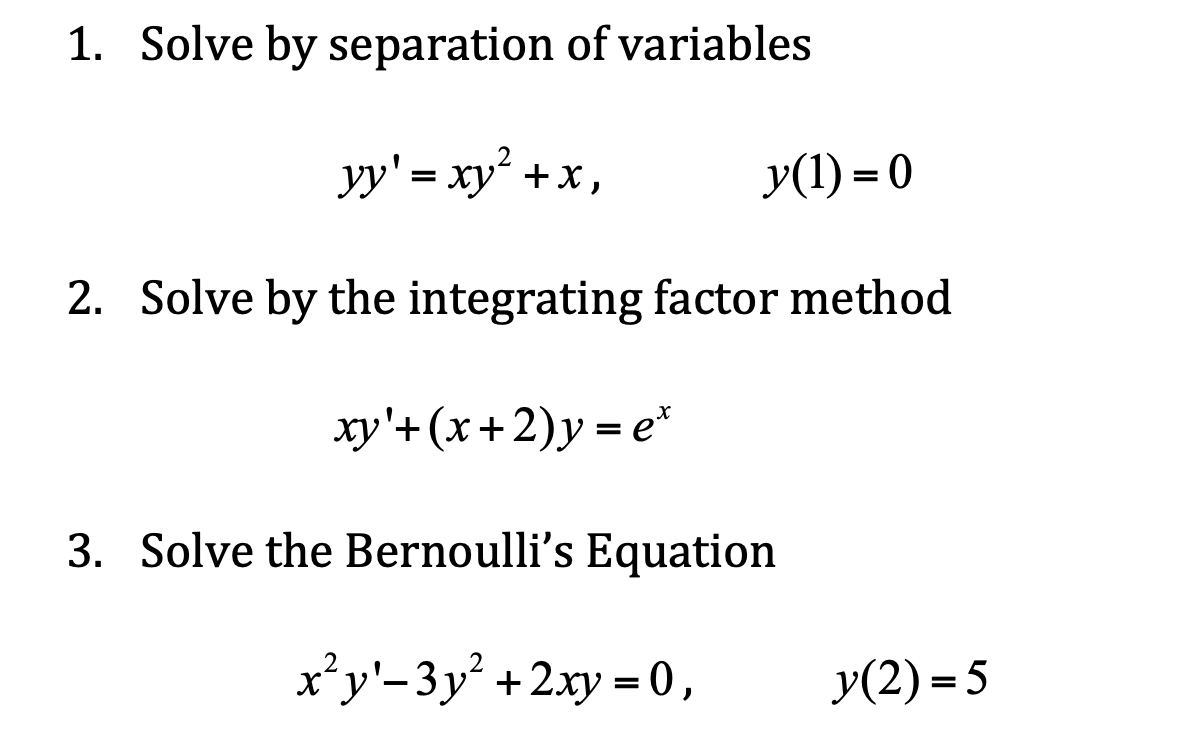


Solved 1 Solve By Separation Of Variables Yy Xy2 X Chegg Com



Factorise 3 12 A B 2 Brainly In
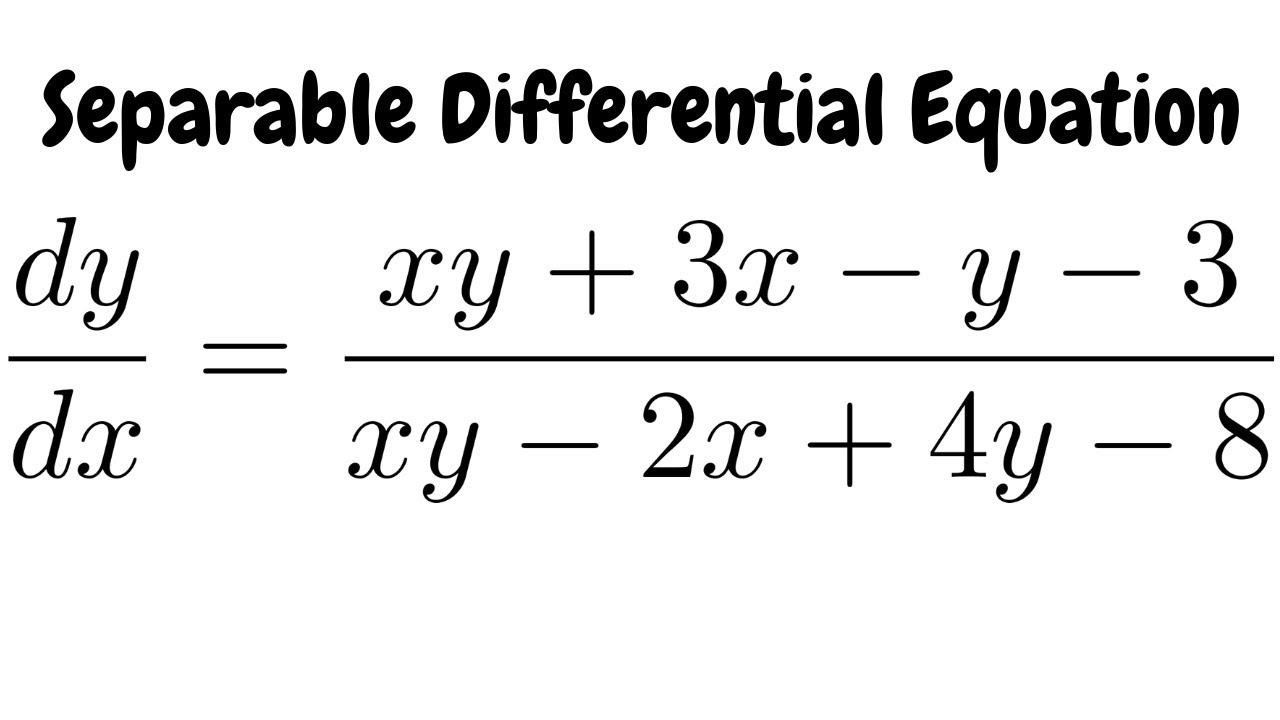


Separable Differential Equation Dy Dx Xy 3x Y 3 Xy 2x 4y 8 Youtube



Exercise 2 4 Question 5 Ncert Solutions Maths Chapter 2 Class 9
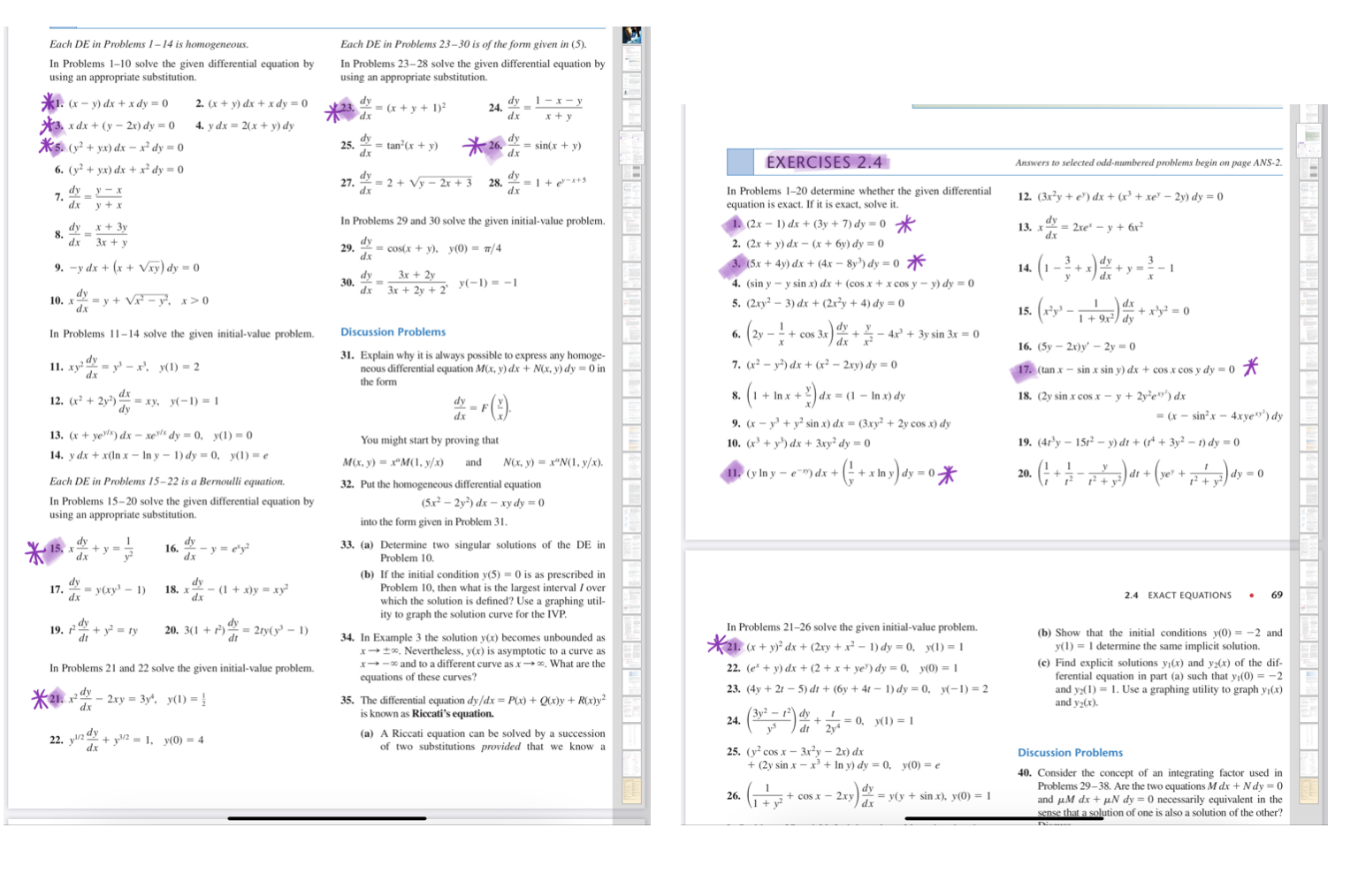


Solved Each De In Problems 1 14 Is Homogeneous In Proble Chegg Com



X 3 3xy 2 Dx Y 3 3x 2y Dy Youtube



If X Y Z 9 And Xy Yz Zx 23 The Value Of X 3 Y 3 Z 3 3xyz Youtube



If X Y Z 6 And Xy Yz Zx 11 And Xyz 6 Is Given Find The Value Of X 3 Y 3 Z 3 Youtube



If X Y 2 3 Find The Value Of 3x 2y 2x 5y



Factorise 3 X Y 2 5 X Y 2 Brainly In


Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Algebraic Expressions Available In Free Pdf Download



Ex 14 1 2 Vi Factorise 5 X 2 Y 15 Xy 2 Chapter 14 Class 8



Ex 2 5 3 Factorise Following Using Appropriate Identities



Find The Products A 3x 2y 4 X X Y 2 Brainly In



If X And Y Are Positive Integers Which Of The Following Problem Solving Ps


10 X Y 2 X Y 4 15 X Y 5 X Y 2 Solve The Pairs Of Equations By Reducing Them To A Pair Of Linear Youtube



Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 14 Factorisation Solutions



If X And Y Are Positive Integers Which Of The Following Problem Solving Ps



Simplify X Y 3 X Y 3 6y X 2 Y 2



Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations Number Chegg Com



Factorise X Cube Minus 2 X Square Y 3 X Y Square Minus 6y Cube Brainly In



Find The Asymptotes Of The Following Curves Y 3 3x 2y X Y 2 3x 3 2y 2 2x Y 4x 5y 6 0 Youtube



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 7 Factorization Download Free Pdf



Factorize I 3 X 2 5 X 2 2 Brainly In


Reorder Factor Levels By Sorting Along Another Variable Fct Reorder Forcats



Factorise X 5 Y 5



Simplifying Algebraic Expressions



Factorize I 3 X 2 5 X 2 2 Brainly In


Chapter 2 A Single Heatmap Complexheatmap Complete Reference



Exact Differential Equations



Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations Number Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿